
Vitamin D is one of the essential vitamins your body needs for overall health. It helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood, aids in bone growth and maintenance, and supports immune function.
Vitamin D has been linked to a number of health benefits, including reducing the risk of some cancers and helping to keep your bones healthy. However, many people don’t get enough vitamin D, which can lead to a number of health problems. In this article, we’ll explore the health benefits of vitamin D and teach you how to get the most out of this important nutrient.
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for human health. It is produced when the sun’s ultraviolet rays hit the human skin.
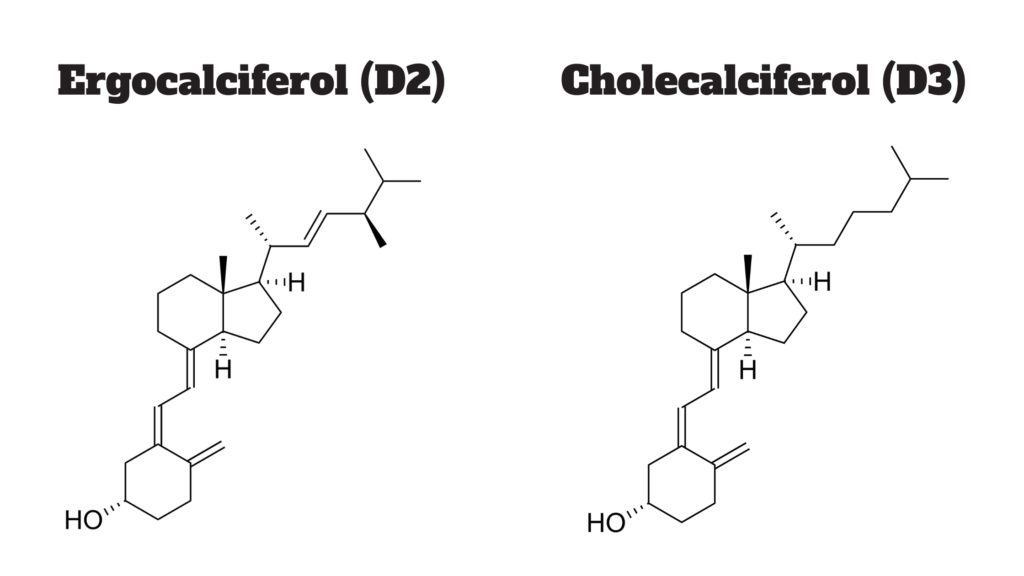
Natural dietary forms of vitamin D are mainly derived from cholesterol. This means that different chemical structures of natural dietary forms of vitamin D can have different effects on the body.
For example, ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) is converted into calcitriol (vitamin D3) in the body. Calcitriol has a shorter half-life than ergocalciferol, so it’s important to consume enough vitamin D2 to maintain a healthy level of calcitriol in the blood.
Another example is cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), which is mainly found in animal products like milk and eggs. Cholecalciferol has a longer half-life than ergocalciferol and calcitriol, so it’s important to avoid excessive consumption of cholecalciferol.
What are the different types of vitamin D?
Not many people know but the term ‘vitamin D’ refers to not one, but several different forms of the vitamin. Saying that only two forms are important in humans: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is the most common form of vitamin D and at the same time, it is the most active form of the nutrient (studies have repeatedly shown that vitamin D3 is superior at raising levels of vitamin D in the body). It is obtained from sun exposure. Vitamin D3 is found in fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, herring, eggs, fortified foods, and supplements.
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is the less active form of the nutrient. It is obtained from sun exposure. Vitamin D2 is a type of vitamin D that is found in plant sources like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds.
What are the health benefits of vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a vitamin that is essential for human health. It is responsible for helping the body to absorb calcium and phosphorus, which are important for bone health. It has also been linked with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and type 1 diabetes. In addition, vitamin D can help promote a healthy immune system.
The health benefits of vitamin D are numerous and include:
- Boosting the immune system
- Preventing diseases, such as cancer, osteoporosis, and depression
- Improving heart health
- Boosting energy levels
- Regulating blood sugar levels
- Reducing inflammation
How can I get more vitamin D?
There are a few ways to get more vitamin D. You can sunbathe, get a supplement, or eat foods with vitamin D. Sunbathing is the best way to get your daily dose of vitamin D.
What are the risks associated with a vitamin D deficiency?
There are a number of health risks associated with a vitamin D deficiency, including:
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke
- Increased risk of cancer
- Increased risk of autoimmune diseases
- Impaired immune function
- Reduced work capacity and increased susceptibility to infections
- Difficulty in regulating body temperature
- Poor absorption of nutrients from food
If you’re not getting enough vitamin D from your diet, supplements may be a good option for you. However, be aware that taking too much vitamin D can also have health risks, so talk to your doctor before taking any supplements.
What are the risks of taking too much vitamin D?
Vitamin D health benefits are well-known, but taking too much can also have risks. Overdose of vitamin D can lead to nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps. It can also cause skin rash and hypercalcemia, a high level of calcium in the blood.
Too much vitamin D can have serious side effects. Some of the most common are:
- High blood pressure.
- High levels of vitamin D can lead to calcium phosphate stones in the kidneys.
- Higher concentrations of vitamin D in the blood have been linked with an increased risk of developing cancer, particularly breast cancer. However, there is not yet enough evidence to say for certain that vitamin D supplementation causes cancer.
- Overdose can cause calcium loss and bone fractures.
- Depression.
- Fatigue.
- Headache.
- Joint pain.
Is there a cure for vitamin D deficiency?
There are a few things that can be done to address vitamin D deficiency. The first thing is to make sure that people are getting enough sunlight. Vitamin D can be acquired through exposure to sunlight, so it is important for people to get out in the sun and get their vitamin D intake from there. Additionally, many foods contain vitamin D, so it is important to eat a balanced diet and include plenty of sources of vitamin D. If people are not getting enough sunlight or food, they can take supplements or supplements with added vitamin D to get their needs met.
How can you test for a vitamin D deficiency?
Testing for a vitamin D deficiency can be done with a blood test or a serum test. A blood test will measure the levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in your blood. A serum test will measure the levels of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D in your blood. If your blood level is below 20 ng/ml, you may have a vitamin D deficiency.
What Is the Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is essential for your body’s absorption of calcium and other nutrients. Some people might not get enough Vitamin D from their diet, so it’s important to take supplements as well. Here is a list of the recommended daily intake for adults:
- 50 IU/day for those who do not have any vitamin D in their diet
- 200 IU/day for pregnant women
- 400 IU/day for breastfeeding women
- 600 IU/day for adults over the age of 18
Foods that contain vitamin D
Foods that contain vitamin D include salmon, tuna, mackerel, Sardines, and herring. Other foods that are high in vitamin D include eggs, cheese, milk, and fortified cereals.
Benefits of eating foods with vitamin D
The human body cannot produce vitamin D on its own and must get it from food. Vitamin D is important for bone health, general well-being, and preventing some types of cancer. A few foods that are high in vitamin D include fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel and tuna, eggs, fortified milk and cereal, and green leafy vegetables.

How to get more vitamin D in your diet
There are many foods that contain vitamin D, but you don’t have to get your daily dose from just one source. Here are five foods that you can add to your diet to boost your vitamin D levels.
1. Fish: Fish is a great source of vitamin D because they are naturally high in nutrient. You can enjoy fish dishes such as grilled salmon or tuna, or try vitamin D-fortified food such as eggs or yoghurt.
2. Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yoghurt all contain vitamin D. You can also top off your breakfast with a sunny-side-up egg or an omelette filled with cheese and diced tomatoes.
3. Oats: Oats are another great source of dietary vitamin D. Add them to your morning oatmeal or granola for a dose of the nutrient.
4. Vegetables: Spinach, Brussels sprouts, and other leafy green vegetables are all good sources of vitamin D. Try adding them to stir-fries, soups, or salads for some extra nutrition and vitamin D intake.
5. Orange juice: One cup of orange juice contains about 100 IU of vitamin D, so it’s a good way to get your daily dose of the nutrient. Add orange juice to your breakfast smoothie or enjoy it as a refreshing drink on its own.
In conclusion
Vitamin D is one of the many essential nutrients your body needs to function properly. Not only does it help maintain overall health, but vitamin D has been linked with a host of other health benefits such as reducing inflammation, helping protect against heart disease and cancer, boosting cognitive function, and so much more. Make sure to get your vitamin D levels checked every year to ensure you are getting the most out of this important nutrient.



[…] of Omega-3 fatty acids, which help to reduce inflammation. In addition, it’s also rich in Vitamin D – which is often lacking in people’s diets. And finally, salmon contains high levels of […]